PCA 从裸机自动化部署 Docker 环境 (PXE + Cloud-init + Ansible)
pxe cloud-init ansible
本实验旨在通过 PXE(Preboot eXecution Environment)、Cloud-Init 和 Ansible 的集成,构建一个高效、自动化的系统部署与配置流程,用于在裸机或虚拟机上实现 Rocky Linux 10.0 的无人值守安装和后续配置管理。整个流程涵盖了从网络引导到操作系统安装,再到动态配置和软件部署的全自动化工作流,适用于快速部署服务器集群或批量配置环境的场景。
PCA(PXE + Cloud-init + Ansible)
自动化操作系统安装:通过 PXE 实现 Rocky Linux 10.0 的网络引导和无人值守安装,基于 Kickstart 配置文件实现标准化的系统部署。
动态初始化配置:利用 Cloud-Init 的 NoCloud 数据源,通过自定义 HTTP 元数据服务器为每台机器动态分配主机名、IP 地址和其他初始化配置。
高级配置管理:通过 Ansible 自动化工具,完成系统后续配置,包括设置软件仓库、安装 Docker 容器环境等,确保系统达到预期的生产状态。
实验环境
操作系统:Alpine Linux v3.22,运行在 PXE 服务器上,内核版本为 6.12.51。
PXE 服务器的网络配置:
- eth0 接口(IP: 192.168.200.139/24)用于外部网络通信,配置了 NAT 转发以支持客户端访问外部网络。
- eth1 接口(IP: 10.33.1.1/16)用于服务 PXE 客户端。
说明:部分脚本由 AI 生成,未经严格测试,可能存在未知错误,仅限实验环境使用,切勿直接用于生产环境。
构建 Alpine PXE 环境
操作系统版本(来源于 /etc/os-release 文件和 uname -a 命令):
NAME="Alpine Linux"
ID=alpine
VERSION_ID=3.22.2
PRETTY_NAME="Alpine Linux v3.22"
HOME_URL="https://alpinelinux.org/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://gitlab.alpinelinux.org/alpine/aports/-/issues"
Linux pxe-server 6.12.51-0-virt #1-Alpine SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC 2025-10-07 15:12:03 x86_64 Linux
网络信息:
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:99:03:b7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.139/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe99:3b7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:99:03:c1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.33.1.1/16 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe99:3c1/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
tftp 服务器
更新系统软件包列表,安装 tftpd-hpa 软件包,这是一个功能增强的 TFTP 服务器。
apk add tftp-hpa
rc-service in.tftpd start
rc-update add in.tftpd default
tftpd-hpa 服务默认为开机自启动。
使用文本编辑器 vim 打开配置文件:
vim /etc/conf.d/in.tftpd
将文件内容修改为如下所示。这些设置将使 TFTP 服务器监听所有网络接口的连接,并允许上传新文件(可选)。
# /etc/init.d/in.tftpd
# Path to server files from
# Depending on your application you may have to change this.
INTFTPD_PATH="/pxe/tftp/"
#INTFTPD_PATH="/var/tftp/"
#INTFTPD_PATH="/tftpboot/"
#INTFTPD_PATH="/tftproot/"
# For more options, see in.tftpd(8)
# -R 4096:32767 solves problems with ARC firmware, and obsoletes
# the /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range hack.
# -s causes $INTFTPD_PATH to be the root of the TFTP tree.
# -l is passed by the init script in addition to these options.
INTFTPD_OPTS="-R 4096:32767 -s ${INTFTPD_PATH} -c -u nobody"
安装 tftpd-hpa 后,如果 /pxe/tftp 目录不存在,则创建该目录。
mkdir -p /pxe/tftp
为了使 TFTP 服务能够管理该目录下的文件,需要将目录的所有者更改为配置文件中指定的 tftp 用户,并赋予适当的读写执行权限。
# 更改目录所有者
chown -R nobody:nobody /pxe/tftp
# 设置目录权限,755 允许所有者读写,其他用户只读
chmod -R 755 /pxe/tftp
注意:有些教程建议使用 777 权限,这会允许任何用户写入,可能带来安全风险。对于大多数应用场景,755 是一个更安全的选择。
若修改了配置文件,应手动重启 tftpd-hpa 服务。
rc-service in.tftpd restart
nginx 服务器
更新软件包列表并安装 nginx 服务。
apk add nginx
rc-service nginx start
rc-update add nginx default
安装成功后会自动启动 Nginx 服务。 nginx 服务默认为开机自启动。
您需要创建一个专门的目录来存放您希望通过 HTTP 提供下载的文件。为了便于管理,我们将其创建在 /srv/http/。
mkdir -p /pxe/http/
为 /pxe/http 目录设置正确的所有权和权限,以确保 Nginx 进程(通常以 www-data 用户身份运行)有权访问这些文件。
# 将目录的所有权递归地赋予 www-data 用户和组
chown -R nginx:nginx /pxe/http
# 确保目录及其中的文件具有正确的读取权限
chmod -R 755 /pxe/http
删除 /etc/nginx/http.d/default.conf 文件
rm -rf /etc/nginx/http.d/default.conf
在 /etc/nginx/http.d/file-server.conf 创建一个新的配置文件。
vim /etc/nginx/http.d/file-server.conf
将以下内容粘贴到您刚刚创建的 file-server 文件中:
server {
listen 80 default_server;
location / {
root /pxe/http/;
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
autoindex_localtime on;
charset utf-8;
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
在重启服务之前,检查配置文件是否存在语法错误。
nginx -t
如果您看到如下输出,则表示配置正确:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
重载 Nginx 服务,以应用所有更改。
rc-service nginx reload
nfs 服务器
安装 NFS 服务器软件包
apk add nfs-utils
rc-service nfs start
rc-update add nfs default
创建一个用于共享的目录,例如 /pxe/nfs:
mkdir -p /pxe/nfs
设置目录权限,确保客户端可以访问(根据需求调整权限):
chown nobody:nobody /pxe/nfs
chmod 755 /pxe/nfs
编辑 NFS 配置文件 /etc/exports,指定共享目录和访问权限:
vim /etc/exports
添加以下内容(根据你的网络和需求调整):
/pxe/nfs 10.33.0.0/16(ro,sync,no_subtree_check)
/pxe/nfs:共享的目录。10.33.0.0/16:允许访问的客户端网络(替换为你的网络范围,例如 192.168.1.* 或特定 IP)。ro:允许读,禁止写。sync:确保数据同步写入。no_subtree_check:禁用子树检查,提高性能。
更新 NFS 导出表:
exportfs -a
kea-dhcp 服务器
更新您的系统软件包列表并安装 Kea DHCPv4 服务器的软件包。
apk add kea-dhcp4
rc-service kea-dhcp4 start
rc-update add kea-dhcp4 default
Kea 的配置文件使用 JSON 格式,默认位于 /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf。我们将备份原始文件并创建一个新的配置。
备份默认配置文件
mv /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf.bak
创建并编辑新的配置文件
vim /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
将下面的 JSON 配置模板完整地复制并粘贴到文件中。您需要根据您的网络环境修改其中的占位符。
{
"Dhcp4": {
"interfaces-config": {
"interfaces": [ "eth1" ]
},
"lease-database": {
"type": "memfile",
"persist": true,
"name": "/var/lib/kea/kea-leases4.csv"
},
"client-classes": [
{
"name": "PXE_BIOS",
"test": "option[93].hex == 0x0000",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "boot-file-name",
"data": "undionly.kpxe"
}
]
},
{
"name": "PXE_UEFI",
"test": "option[93].hex == 0x0007 or option[93].hex == 0x0009",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "boot-file-name",
"data": "ipxe.efi"
}
]
}
],
"subnet4": [
{
"id": 1,
"subnet": "10.33.0.0/16",
"pools": [
{
"pool": "10.33.1.100 - 10.33.1.200"
}
],
"next-server": "10.33.1.1",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "10.33.1.1"
},
{
"name": "domain-name-servers",
"data": "223.5.5.5, 223.6.6.6"
}
],
"valid-lifetime": 4000,
"renew-timer": 1000,
"rebind-timer": 2000,
}
],
"loggers": [
{
"name": "kea-dhcp4",
"output_options": [
{
"output": "/var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log"
}
],
"severity": "INFO",
"debuglevel": 0
}
]
}
}
如果修改了配置文件,需重启服务以应用更改。
rc-service kea-dhcp4 restart
挂载 ISO 镜像
将 ISO 镜像连接到 PXE 服务器,并设置开机自动挂载到 /pxe/http/rocky10.0 文件夹。
创建 /pxe/http/rocky10.0 文件夹
mkdir /pxe/http/rocky10.0
使用 blkid 命令查看该 ISO 设备的是否正常添加。
# blkid
/dev/sr0: BLOCK_SIZE="2048" UUID="2025-05-31-19-44-34-00" LABEL="Rocky-10-0-x86_64-dvd" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="PMBR"
编辑 /etc/fstab 文件在文件末尾添加以下内容:
vim /etc/fstab
/dev/sr0 /pxe/http/rocky10.0 iso9660 loop,ro 0 0
使挂载生效:
mount -a
查看 /pxe/http/rocky10.0 文件夹,检查是否挂载成功:
# ls /pxe/http/rocky10.0/
AppStream EULA boot
BaseOS LICENSE extra_files.json
COMMUNITY-CHARTER RPM-GPG-KEY-Rocky-10 images
EFI RPM-GPG-KEY-Rocky-10-Testing media.repo
配置 boot 文件
将 ISO 镜像中的 vmlinuz 和 initrd.img 文件复制到 /pxe/http/boot 文件夹中。
vmlinuz 和 initrd.img 文件存在于 ISO 中的两个路径下,比对文件的 SHA256 值,两个路径下的文件完全一致:
/images/pxeboot/vmlinuz
/images/pxeboot/initrd.img
/isolinux/vmlinuz
/isolinux/initrd.img
注意:此处的根路径指的是 ISO 文件的根路径,而非系统文件中的根路径,系统文件的根路径为 /pxe/http/rocky10.0/…
创建 /pxe/http/boot 文件夹。
mkdir /pxe/http/boot/ -p
复制文件到 /pxe/http/boot 文件夹中,此处选择复制 /pxe/http/rocky10.0/images/pxeboot 路径中的文件。
cp /pxe/http/rocky10.0/images/pxeboot/vmlinuz /pxe/http/boot/vmlinuz
cp /pxe/http/rocky10.0/images/pxeboot/initrd.img /pxe/http/boot/initrd.img
设置 /pxe/http/boot 文件夹,以及 vmlinuz 和 initrd.img 文件的权限。
chown -R nginx:nginx /pxe/http/boot
配置 iptables 规则
配置 iptables 规则并开启 ip 转发。
安装 iptables 工具和服务。
apk add iptables
清空现有规则
iptables -F
iptables -t nat -F
为 10.33.0.0/16 网段的流量启用 NAT 转发:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.33.0.0/16 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
配置 FORWARD 规则,允许 eth0 和 eth1 之间的双向流量转发:
iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o eth1 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -i eth1 -o eth0 -j ACCEPT
注意:上述配置适用于 filter 表中 FORWARD 链默认策略为 DROP 的情况。Alpine Linux 系统默认策略为 ACCEPT。
保存 iptables 规则
rc-service iptables save
编辑 /etc/conf.d/iptables,进行以下更改:
vim /etc/conf.d/iptables
- 将 SAVE_ON_STOP 设置为 no。
- 将 IPFORWARD 设置为 yes。
修改后的配置文件内容如下:
# /etc/conf.d/iptables
# Location in which iptables initscript will save set rules on
# service shutdown
IPTABLES_SAVE="/etc/iptables/rules-save"
# Options to pass to iptables-save and iptables-restore
SAVE_RESTORE_OPTIONS="-c"
# Save state on stopping iptables
SAVE_ON_STOP="no"
# Enable/disable IPv4 forwarding with the rules
IPFORWARD="yes"
启动 iptables 服务并添加到开机自启动。
rc-service iptables start
rc-update add iptables default
编写 ks 文件
anaconda-ks.cfg 是一个用于 Red Hat 系列 Linux 发行版(如 CentOS、Fedora、RHEL 等)的 Kickstart 配置文件。它是由 Anaconda 安装程序在系统安装完成后自动生成的文件,通常位于 /root 目录下。
这个文件可以作为模板,用于创建自定义的 Kickstart 文件。通过修改 anaconda-ks.cfg,用户可以生成一个新的 Kickstart 文件,用于在其他机器上实现自动化、无交互的系统安装。
以下 anaconda-ks.cfg 是从新安装的 rocky10.0 系统(基于 UEFI)中的 /root/ 路径下读取的。
注意:这个文件是基于 UEFI,不能直接用于 Legacy BIOS,尤其是磁盘部分的配置。
# Generated by Anaconda 40.22.3.26
# Generated by pykickstart v3.52.8
#version=RHEL10
# Use graphical install
graphical
%addon com_redhat_kdump --enable --reserve-mb='auto'
%end
# Keyboard layouts
keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='cn'
# System language
lang zh_CN.UTF-8 --addsupport=en_US.UTF-8
# Network information
network --bootproto=dhcp --device=ens33 --noipv6 --activate
repo --name="AppStream" --baseurl=file:///run/install/repo/AppStream
%packages
@^minimal-environment
%end
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
firstboot --enable
# Generated using Blivet version 3.10.0
ignoredisk --only-use=sda
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --none --initlabel
# Disk partitioning information
part /boot/efi --fstype="efi" --ondisk=sda --size=1024 --fsoptions="umask=0077,shortname=winnt"
part pv.48 --fstype="lvmpv" --ondisk=sda --size=100350
part /boot --fstype="xfs" --ondisk=sda --size=1024
volgroup rl --pesize=4096 pv.48
logvol / --fstype="xfs" --size=100348 --name=root --vgname=rl
# System timezone
timezone Asia/Shanghai --utc
# Root password
rootpw --iscrypted --allow-ssh $y$j9T$3Ps2KZhmIBuEoqfziQ95h8uB$fs/fRxMH91mIDDBk1pLDYjTtOKHEUG6THsXJOmf1gR2
将该文件作为模板文件进行修改,制作自定义的文件。
将第 6 行的 graphical 命令注释掉(在行首添加 #)。 在第 6 行新增 text 命令。
4 # Use graphical install
- 5 graphical
+ 5 # graphical
+ 6 text
7
原始配置使用图形化界面(GUI)进行安装。注释掉 graphical 并添加 text 命令,将安装程序切换到文本模式(TUI),这在自动化或服务器安装中更常见。
将第 13 行的 keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='cn' 修改为 keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='us'。
12 # Keyboard layouts
- 13 keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='cn'
+ 13 keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='us'
14 # System language
原始配置将 X Window System 键盘布局(xlayouts)设置为 ‘cn’ (中文)。修改后的配置将其更改为 ‘us’ (美国英语),这在服务器(尤其是文本模式)环境中更常用。
将第 15 行的 lang zh_CN.UTF-8 --addsupport=en_US.UTF-8 修改为 lang en_US.UTF-8。
14 # System language
- 15 lang zh_CN.UTF-8 --addsupport=en_US.UTF-8
+ 15 lang en_US.UTF-8
16
原始配置将系统默认语言设置为 ‘zh_CN.UTF-8’ (简体中文),并额外支持 ‘en_US.UTF-8’。修改后的配置将默认语言直接设置为 ‘en_US.UTF-8’ (美国英语),以确保服务器环境的兼容性和一致性。
将第 20 行的 repo 命令注释掉(在行首添加 #)。 在第 20 行新增 url --url=http://10.33.1.1/rocky10.0。
19
- 20 repo --name="AppStream" --baseurl=file:///run/install/repo/AppStream
+ 20 # repo --name="AppStream" --baseurl=file:///run/install/repo/AppStream
+ 21
+ 22 url --url=http://10.33.1.1/rocky10.0
23
原始配置使用本地安装介质中的仓库(file:///run/install/repo/AppStream)。注释掉 repo 并添加 url 命令,指示安装程序从指定的网络地址(http://10.33.1.1/rocky10.0)获取所有安装文件和仓库信息,这是实现 PXE 网络安装的关键。
在 %packages 区域中(第 26 行后)新增 cloud-init 包。
24 %packages
25 @^minimal-environment
+ 26 cloud-init
27
28 %end
在最小化安装(@^minimal-environment)的基础上,额外安装 cloud-init 软件包。cloud-init 用于在系统首次启动时从数据源(如 http 服务器)获取配置并自动执行任务。
将第 31 行的 firstboot --enable 修改为 firstboot --disable。
30 # Run the Setup Agent on first boot
- 31 firstboot --enable
+ 31 firstboot --disable
32
firstboot --enable 会在系统首次启动时运行一个交互式的设置代理程序(Setup Agent)。在自动化安装中,我们希望系统启动后立即可用,因此使用 firstboot --disable 禁用这个功能。
将第 36 行的 clearpart --none --initlabel 修改为 clearpart --all --initlabel。
35 # Partition clearing information
- 36 clearpart --none --initlabel
+ 36 clearpart --all --initlabel
37 # Disk partitioning information
clearpart --none 保留磁盘上的现有分区。clearpart --all 指示安装程序在安装前清除磁盘上的所有分区和数据,确保在目标磁盘上进行全新的、干净的安装。
在文件末尾(rootpw 命令之后)添加了一个 %post 脚本块。
... (rootpw line) ...
+
+ %post --log=/root/ks-post.log
+
+ cat << EOF > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
+ # The modules that run in the 'init' stage
+ cloud_init_modules:
+ - seed_random
+ - bootcmd
+ - write_files
+ - growpart
+ - resizefs
+ - disk_setup
+ - mounts
+ - set_hostname
+ - update_hostname
+ - update_etc_hosts
+ - ca_certs
+ - rsyslog
+ - users_groups
+ - ssh
+ - set_passwords
+
+ # The modules that run in the 'config' stage
+ cloud_config_modules:
+ - ssh_import_id
+ - locale
+ - rh_subscription
+ - spacewalk
+ - yum_add_repo
+ - ntp
+ - timezone
+ - disable_ec2_metadata
+ - runcmd
+
+ # The modules that run in the 'final' stage
+ cloud_final_modules:
+ - package_update_upgrade_install
+ - write_files_deferred
+ - puppet
+ - chef
+ - ansible
+ - mcollective
+ - salt_minion
+ - reset_rmc
+ - scripts_vendor
+ - scripts_per_once
+ - scripts_per_boot
+ - scripts_per_instance
+ - scripts_user
+ - ssh_authkey_fingerprints
+ - keys_to_console
+ - install_hotplug
+ - phone_home
+ - final_message
+ - power_state_change
+ EOF
+
+ cat << EOF > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99_datasource_list.cfg
+ datasource_list: [ NoCloud, None ]
+
+ datasource:
+ NoCloud:
+ seedfrom: http://10.33.1.1:8080/
+ EOF
+
+ %end
新增了 %post 脚本,该脚本在系统安装完成后、首次重启前运行。此脚本用于配置 cloud-init:
- 创建
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg配置文件,定义cloud-init在不同阶段(init, config, final)运行的模块。 - 创建
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99_datasource_list.cfg来指定cloud-init的数据源为NoCloud,并指示它从http://10.33.1.1:8080/获取配置数据(user-data, meta-data)。
在 Kickstart 文件的最后一行添加 reboot 命令。
... (%end of post script) ...
+
+ reboot
添加 reboot 确保安装过程成功结束后,系统自动重启,进入新安装的操作系统环境,这是自动化流程的最后一步。
写入 ks 文件
创建 /pxe/http/config 文件夹,在 /pxe/http/config/anaconda-ks.cfg 创建文件,写入修改后的 anaconda-ks.cfg 完整文件。
mkdir /pxe/http/config -p
vim /pxe/http/config/anaconda-ks.cfg
# Generated by Anaconda 40.22.3.26
# Generated by pykickstart v3.52.8
#version=RHEL10
# Use graphical install
# graphical
text
%addon com_redhat_kdump --enable --reserve-mb='auto'
%end
# Keyboard layouts
keyboard --vckeymap=cn --xlayouts='us'
# System language
lang en_US.UTF-8
# Network information
network --bootproto=dhcp --device=ens33 --noipv6 --activate
# repo --name="AppStream" --baseurl=file:///run/install/repo/AppStream
url --url=http://10.33.1.1/rocky10.0
%packages
@^minimal-environment
cloud-init
%end
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
firstboot --disable
# Generated using Blivet version 3.10.0
ignoredisk --only-use=sda
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --all --initlabel
# Disk partitioning information
part /boot/efi --fstype="efi" --ondisk=sda --size=1024 --fsoptions="umask=0077,shortname=winnt"
part pv.48 --fstype="lvmpv" --ondisk=sda --size=100350
part /boot --fstype="xfs" --ondisk=sda --size=1024
volgroup rl --pesize=4096 pv.48
logvol / --fstype="xfs" --size=100348 --name=root --vgname=rl
# System timezone
timezone Asia/Shanghai --utc
# Root password
rootpw --iscrypted --allow-ssh $y$j9T$3Ps2KZhmIBuEoqfziQ95h8uB$fs/fRxMH91mIDDBk1pLDYjTtOKHEUG6THsXJOmf1gR2
%post --log=/root/ks-post.log
cat << EOF > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
# The modules that run in the 'init' stage
cloud_init_modules:
- seed_random
- bootcmd
- write_files
- growpart
- resizefs
- disk_setup
- mounts
- set_hostname
- update_hostname
- update_etc_hosts
- ca_certs
- rsyslog
- users_groups
- ssh
- set_passwords
# The modules that run in the 'config' stage
cloud_config_modules:
- ssh_import_id
- locale
- rh_subscription
- spacewalk
- yum_add_repo
- ntp
- timezone
- disable_ec2_metadata
- runcmd
# The modules that run in the 'final' stage
cloud_final_modules:
- package_update_upgrade_install
- write_files_deferred
- puppet
- chef
- ansible
- mcollective
- salt_minion
- reset_rmc
- scripts_vendor
- scripts_per_once
- scripts_per_boot
- scripts_per_instance
- scripts_user
- ssh_authkey_fingerprints
- keys_to_console
- install_hotplug
- phone_home
- final_message
- power_state_change
EOF
cat << EOF > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99_datasource_list.cfg
datasource_list: [ NoCloud, None ]
datasource:
NoCloud:
seedfrom: http://10.33.1.1:8080/
EOF
%end
reboot
注意:这个文件是基于 UEFI,不能直接用于 Legacy BIOS,尤其是磁盘部分的配置。
设置 /pxe/http/config 文件夹,以及 anaconda-ks.cfg 文件的权限。
chown -R nginx:nginx /pxe/http/config
编译 ipxe NBP 文件
在开始编译之前,您需要一个安装了必要开发工具的 Linux 环境。如果您使用的是基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版,可以运行以下命令安装所需的依赖包:
apk add build-base perl git xz-dev
在某些地区,GitHub 访问速度可能较慢,可通过以下命令配置 SOCKS5 代理(仅适用于 HTTP 和 HTTPS 协议,不支持 SSH 协议):
git config --global http.proxy "socks5://127.0.0.1:1080"
git config --global https.proxy "socks5://127.0.0.1:1080"
注意:请将 127.0.0.1:1080 替换为实际的代理地址和端口。
从官方仓库克隆 iPXE 的源代码:
cd /root/
git clone https://github.com/ipxe/ipxe.git
切换到源代码目录
cd ipxe/src
在 src 目录下,创建一个名为 boot.ipxe 的文件。这个文件将包含您希望 iPXE 在启动时执行的指令。
编写 boot.ipxe 文件并编译 ipxe NBP 文件。
vim boot.ipxe
这是一个 boot.ipxe 文件的示例,您可以根据自己的需求进行修改:
#!ipxe
dhcp
set server-ip 10.33.1.1
set initrd http://${server-ip}/boot/initrd.img
set vmlinuz http://${server-ip}/boot/vmlinuz
set repo http://${server-ip}/rocky10.0
set ks-config http://${server-ip}/config/anaconda-ks.cfg
kernel ${vmlinuz}
initrd ${initrd}
imgargs vmlinuz \
initrd=initrd.img \
ip=dhcp \
inst.repo=${repo} \
inst.ks=${ks-config}
boot
在 /root/ipxe/src 路径下创建 install.sh 脚本,在修改 boot.ipxe 文件执行该脚本,自动编译为 NBP 文件并复制到目标位置。
vim install.sh
#!/bin/sh
TARGET=/pxe/tftp
cd /root/ipxe/src/
make bin-x86_64-efi/ipxe.efi EMBED=boot.ipxe -j 2
make bin/undionly.kpxe EMBED=boot.ipxe -j 2
cp -p bin-x86_64-efi/ipxe.efi $TARGET
cp -p bin/undionly.kpxe $TARGET
chown -R nobody:nobody $TARGET
chmod 644 $TARGET/*
为 install.sh 添加可执行权限并执行。
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh
检查 ipxe NBP 文件是否编译成功,并复制到了目标位置。
# ls -la /pxe/tftp/
..
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 1013760 Oct 20 08:47 ipxe.efi
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 70569 Oct 20 08:47 undionly.kpxe
cloud-init 元数据服务器
cloud-init 是 Linux 虚拟机和裸机实例在首次启动时进行初始化的行业标准工具。它在系统启动的早期阶段运行,从一个”数据源”(Datasource)获取配置数据,然后根据这些数据来配置系统。
cloud-init 可以自动化处理各种初始设置任务,包括:
- 设置主机名(Hostname)
- 配置网络接口
- 创建用户账户并设置密码
- 添加 SSH 公钥
- 安装软件包
- 运行任意脚本(
runcmd)
这是一个非常棒的自动化部署工作流。您正在使用 cloud-init 的 NoCloud 数据源,配合一个自定义的 Python HTTP 服务器,来实现对裸机(或虚拟机)的动态、自动化的配置。
以下是您提供的内容的优化版本,增加了关于 cloud-init 及其元数据服务器的介绍,并详细说明了您的实现步骤。
什么是 cloud-init?
cloud-init 是 Linux 虚拟机和裸机实例在首次启动时进行初始化的行业标准工具。它在系统启动的早期阶段运行,从一个”数据源”(Datasource)获取配置数据,然后根据这些数据来配置系统。
cloud-init 可以自动化处理各种初始设置任务,包括:
- 设置主机名(Hostname)
- 配置网络接口
- 创建用户账户并设置密码
- 添加 SSH 公钥
- 安装软件包
- 运行任意脚本(
runcmd)
元数据服务器(Metadata Server)就是 cloud-init 用来获取配置数据的”数据源”。
此处创建了一个自定义的元数据服务器,使用 NoCloud 数据源类型,它指示 cloud-init 从一个简单的 HTTP URL(在您的 Kickstart 文件中配置为 http://10.33.1.1:8080/)来获取数据。
这个服务器必须提供至少两个文件:
meta-data:包含实例的唯一信息,如instance-id和local-hostname。user-data:包含#cloud-configYAML 文件,定义了要执行的配置任务(如添加 SSH 密钥、运行命令)。
server.py 脚本就是一个轻量级、智能的元数据服务器。它根据请求的客户端 IP 地址,动态地生成 meta-data 文件,为每台机器提供专属的主机名和 ID。
首先,我们创建 cloud-init 需要的配置数据。我们将所有数据文件存放在 /opt/cloud-init/web/ 目录中,server.py 将从这里提供文件。
mkdir /opt/cloud-init/web/ -p
cd /opt/cloud-init/web/
# 创建所有必需的文件
# vendor-data 和 network-config 在此场景中可以为空,但必须存在
touch user-data meta-data vendor-data network-config
生成一个4096位RSA密钥对,并将私钥保存到 /root/.ssh/ssh_key,公钥保存到 /root/.ssh/ssh_pub
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f /root/.ssh/ssh_key -N ""
生成后,公钥文件默认是 ssh_key.pub,需要重命名为 /root/.ssh/ssh_pub
mv /root/.ssh/ssh_key.pub /root/.ssh/ssh_pub
user-data 是 cloud-init 的核心配置,使用 #cloud-config YAML 格式。
将 user-data 中 ssh_authorized_keys 的 xxx 替换为 ssh_pub 文件中的内容。
vim user-data
#cloud-config
preserve_hostname: false
disable_root: false
ssh_pwauth: false
users:
- name: root
lock_passwd: false
ssh_authorized_keys:
- xxx
ssh_deletekeys: true
ssh_genkeytypes: ['rsa', 'ecdsa', 'ed225519']
runcmd:
# 使用 'sh -c' 来执行一个包含 shell 逻辑 (如循环) 的命令
# 使用 'until' 循环来确保回调成功,防止服务器 (10.33.1.1) 暂时不可达
# -sf: -s (silent) 安静模式, -f (fail) 在 HTTP 4xx/5xx 错误时返回失败 (非0)
- ['sh', '-c', 'until curl -sf http://10.33.1.1:8081/ready; do echo "Callback failed, retrying in 5s..."; sleep 5; done']
meta-data 是一个模板文件。server.py 会读取它,并动态替换占位符 <...>。
vim meta-data
instance-id: <instance-id>
local-hostname: <local-hostname>
现在,我们在 /opt/cloud-init/ 目录中创建数据源和管理脚本。
cd /opt/cloud-init/
touch instance.csv server.py generate-kea-config.sh
instance.csv 是所有服务器的清单。server.py 和 generate-kea-config.sh 都会读取此文件。 格式: instance_id,hostname,ip,mac。
vim instance.csv
docker-01,docker-01,10.33.1.101,00:0C:29:66:2C:AF
docker-02,docker-02,10.33.1.102,00:0C:29:FC:03:13
docker-03,docker-03,10.33.1.103,00:0c:29:66:2c:b9
注意:需要将文件中的 MAC 地址替换为客户机网卡实际 MAC 地址。
generate-kea-config.sh 脚本读取 instance.csv 并自动生成 Kea DHCP 的配置文件,为每个 MAC 地址创建静态 IP 预留。
vim generate-kea-config.sh
#!/bin/sh
# --- 配置路径 ---
CSV_FILE="instance.csv"
FINAL_CONFIG="/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf"
# ---
echo "正在生成 Kea 配置文件: $FINAL_CONFIG"
# 1. 将 "头部" 模板硬编码并写入新配置 (覆盖)
cat > "$FINAL_CONFIG" << 'EOF'
{
"Dhcp4": {
"interfaces-config": {
"interfaces": [ "eth1" ]
},
"lease-database": {
"type": "memfile",
"persist": true,
"name": "/var/lib/kea/kea-leases4.csv"
},
"client-classes": [
{
"name": "PXE_BIOS",
"test": "option[93].hex == 0x0000",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "boot-file-name",
"data": "undionly.kpxe"
}
]
},
{
"name": "PXE_UEFI",
"test": "option[93].hex == 0x0007 or option[93].hex == 0x0009",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "boot-file-name",
"data": "ipxe.efi"
}
]
}
],
"subnet4": [
{
"id": 1,
"subnet": "10.33.0.0/16",
"pools": [
{
"pool": "10.33.1.100 - 10.33.1.200"
}
],
"next-server": "10.33.1.1",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "10.33.1.1"
},
{
"name": "domain-name-servers",
"data": "223.5.5.5, 223.6.6.6"
}
],
"valid-lifetime": 4000,
"renew-timer": 1000,
"rebind-timer": 2000,
EOF
# 'EOF' 标志结束
# 2. 运行 awk 命令,从 CSV 生成 reservations 块 (追加)
# (注意: 我们只使用第3列(IP)和第4列(MAC))
awk -F, '
BEGIN {
print " \"reservations\": ["
}
{
if (NR > 1) {
print ","
}
printf " {\n"
printf " \"hw-address\": \"%s\",\n", $4
printf " \"ip-address\": \"%s\"\n", $3
printf " }"
}
END {
print "\n ]"
}
' "$CSV_FILE" >> "$FINAL_CONFIG"
# 3. <--- 错误的多余逗号已被移除 --->
# (之前这里有一行 echo "," >> "$FINAL_CONFIG")
# 4. 将 "尾部" 模板硬编码 (追加)
# (这个模板现在紧跟在 awk 生成的 "reservations" 数组后面)
cat >> "$FINAL_CONFIG" << 'EOF'
}
],
"loggers": [
{
"name": "kea-dhcp4",
"output_options": [
{
"output": "/var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log"
}
],
"severity": "INFO",
"debuglevel": 0
}
]
}
}
EOF
# 'EOF' 标志结束
echo "配置文件已生成。"
# 5. (重要!) 检查配置并重载服务
echo "正在验证配置..."
if kea-dhcp4 -t "$FINAL_CONFIG" 2>&1 > /dev/null; then
echo "配置有效。正在重载 kea-dhcp4 服务..."
# 适用于 Alpine Linux (OpenRC)
rc-service kea-dhcp4 restart
echo "服务已重载。"
else
echo "错误:生成的配置文件无效!Kea 服务未重载。"
echo "请检查 $FINAL_CONFIG 的语法。"
exit 1
fi
执行 generate-kea-config.sh 脚本,生成 /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf 配置文件,更新 DHCP 配置,以确保机器在 PXE 引导时能获取到正确的 IP 地址。(请确保脚本有执行权限: chmod +x generate-kea-config.sh)
chmod +x generate-kea-config.sh
./generate-kea-config.sh
server.py 脚本将作为 NoCloud 数据源的 HTTP 服务器。
vim server.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import http.server
import socketserver
import csv
import os
from pathlib import Path
PORT = 8080
BIND_ADDR = '10.33.1.1'
DATA_DIR = 'web' # 修改此路径来改变 user-data、vendor-data 等文件位置
DATA_FILE = 'instance.csv' # 修改此路径来改变 instance.csv 位置,默认读取当前工作路径
# 加载CSV数据库
def load_instances():
instances = {}
if not os.path.exists(DATA_FILE):
return instances
try:
with open(DATA_FILE, 'r') as f:
reader = csv.DictReader(f, fieldnames=['instance_id', 'hostname', 'ip', 'mac'])
for row in reader:
if row and row['ip']:
instances[row['ip']] = {
'instance_id': row['instance_id'],
'hostname': row['hostname'],
'mac': row['mac']
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading CSV: {e}")
return instances
INSTANCES = load_instances()
class MetadataHandler(http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
client_ip = self.client_address[0]
try:
if self.path == '/meta-data':
self.serve_metadata(client_ip)
elif self.path in ['/vendor-data', '/user-data', '/network-config']:
self.serve_file(self.path[1:])
else:
self.send_error(404)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
self.send_error(500)
def serve_metadata(self, client_ip):
if client_ip not in INSTANCES:
self.send_error(404, "Instance not found")
return
instance = INSTANCES[client_ip]
meta_file = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'meta-data')
if not os.path.exists(meta_file):
self.send_error(404, "meta-data file not found")
return
try:
with open(meta_file, 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
# 替换占位符
content = content.replace('<instance-id>', instance['instance_id'])
content = content.replace('<local-hostname>', instance['hostname'])
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'text/plain')
self.send_header('Content-Length', len(content.encode()))
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(content.encode())
except Exception as e:
self.send_error(500)
def serve_file(self, filename):
filepath = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
self.send_error(404)
return
try:
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
content = f.read()
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'application/octet-stream')
self.send_header('Content-Length', len(content))
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(content)
except Exception as e:
self.send_error(500)
def log_message(self, format, *args):
print(f"[{self.client_address[0]}] {format % args}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
with socketserver.TCPServer((BIND_ADDR, PORT), MetadataHandler) as httpd:
print(f"Server running on {BIND_ADDR}:{PORT}")
httpd.serve_forever()
为 server.py 脚本设置可执行权限,并执行脚本,运行元数据服务器。
chmod +x server.py
./server.py
ansible
在您的自动化流程中,cloud-init 负责完成最基础的系统设置(主机名、网络、SSH密钥)。一旦机器准备就绪,它就需要一个更强大的工具来执行复杂的软件安装、配置和服务管理。此时可以使用 Ansible 工具。
Ansible 是一个开源的 IT 自动化工具,它可以配置系统、部署软件和编排更高级的 IT 任务(如持续部署或零停机滚动更新)。它使用声明性的 YAML 语言来描述系统应有的状态,并通过 SSH(默认)连接到受管节点来执行这些配置。
为安装 ansible-core 等工具,需启用 Alpine Linux 的社区软件仓库。
编辑 /etc/apk/repositories 文件,查找并取消注释 http://xxx/alpine/v3.22/community 行(移除行首的 #)。
或者,直接用以下内容覆盖文件:
vim /etc/apk/repositories
#/media/cdrom/apks
http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/alpine/v3.22/main
http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/alpine/v3.22/community
安装 ansible-core 工具
apk add ansible-core
在服务器上,创建 /opt/ansible/ 目录并创建文件。
mkdir /opt/ansible/ -p
cd /opt/ansible/
touch configure_repos.yaml centos_docker_china.yaml rocky10.repo.j2 ready.py
rocky10.repo.j2 是一个 Jinja2 模板文件。
Ansible 使用它来动态生成配置文件。{{ baseurl }} 和 {{ gpgkey }} 是变量,在 configure_repos.yaml 中被定义和传入。这种方式使得配置更加灵活和可维护。
vim rocky10.repo.j2
[rocky10-base]
name=Rocky10 Base Repository
baseurl={{ baseurl }}/BaseOS/$basearch/os/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey={{ gpgkey }}
[rocky10-appstream]
name=Rocky10 AppStream Repository
baseurl={{ baseurl }}/AppStream/$basearch/os/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey={{ gpgkey }}
configure_repos.yaml Playbook 负责第一阶段的配置,它首先会移除所有默认的 .repo 文件,然后使用 rocky10.repo.j2 模板生成一个指向阿里云镜像的、干净的配置文件。
vim configure_repos.yaml
---
- name: Configure YUM repositories on Rocky Linux 10
hosts: centos # 替换为您的 inventory 主机组
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Remove default Rocky repositories
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: absent
loop:
- /etc/yum.repos.d/rocky-addons.repo
- /etc/yum.repos.d/rocky-devel.repo
- /etc/yum.repos.d/rocky-extras.repo
- /etc/yum.repos.d/rocky.repo
notify: Clean DNF cache
- name: Add rocky10 repository
vars:
baseurl: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/rockylinux/10.0 # 替换为实际镜像站点
gpgkey: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/rockylinux/RPM-GPG-KEY-Rocky-10
template:
src: rocky10.repo.j2
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/rocky10.repo
owner: root
group: root
mode: '0644'
backup: yes
notify: Clean DNF cache
- name: Update DNF cache
ansible.builtin.dnf:
update_cache: yes
handlers:
- name: Clean DNF cache
command: dnf clean all
centos_docker_china.yaml Playbook 负责第二阶段的配置。
首先检查操作系统是否符合要求,以及 Docker 是否已经安装。如果已安装,任务会跳过,不会做任何改变。
如果未安装,它会添加 Docker 的 YUM/DNF 仓库,安装所有必需的软件包。
创建 daemon.json 配置文件,并确保 Docker 服务启动并设置为开机自启。
vim centos_docker_china.yaml
---
- name: 部署 Docker 容器环境
hosts: centos
vars:
# 定义需要检查的软件包列表
docker_required_packages:
- yum-utils
- device-mapper-persistent-data
- lvm2
docker_packages:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
- containerd.io
- docker-buildx-plugin
- docker-compose-plugin
tasks:
- name: 操作系统信息
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: >-
操作系统是 {{ ansible_distribution }} 版本是 {{ ansible_distribution_version }}
{% if ansible_distribution in ['CentOS', 'RedHat', 'Rocky'] %}
符合要求,准备部署 Docker
{% else %}
不符合部署要求,正在结束
{% endif %}
- name: 操作系统不符合,结束部署
ansible.builtin.meta: end_host
when: ansible_distribution not in ['CentOS', 'RedHat', 'Rocky']
- name: 获取软件包列表
ansible.builtin.package_facts:
manager: auto
- name: 检查主机是否安装 Docker
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
installed_docker_packages: "{{ docker_packages | intersect(ansible_facts.packages.keys()) }}"
- name: Docker 安装情况
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: installed_docker_packages
when: installed_docker_packages
- name: Docker 已经安装,结束部署
ansible.builtin.meta: end_host
when: installed_docker_packages
- name: 检查 /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo 文件是否存在
ansible.builtin.stat:
path: /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
register: docker_repo_file
- name: 添加 Docker 软件仓库 (适用于 CentOS/RedHat/Rocky)
block:
- name: 确保 yum-utils, device-mapper-persistent-data, lvm2 已安装
ansible.builtin.yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop: "{{ docker_required_packages }}"
- name: 下载 Docker YUM 源配置文件
ansible.builtin.get_url:
url: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
mode: '0644'
- name: 替换为阿里云镜像地址
ansible.builtin.replace:
path: /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
regexp: 'download.docker.com'
replace: 'mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce'
- name: 清理 YUM 缓存
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: yum clean all
changed_when: false
- name: 更新 YUM 缓存
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: yum makecache
changed_when: false
- name: 设置仓库已添加的标记
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
docker_repo_added: true
when: not docker_repo_file.stat.exists
- name: 安装并启动 Docker
block:
- name: CentOS 安装 Docker 软件包
ansible.builtin.yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop: "{{ docker_packages }}"
register: docker_install_result
- name: 确保 /etc/docker 目录存在
ansible.builtin.file:
path: /etc/docker
state: directory
mode: '0755'
- name: 更新 /etc/docker/daemon.json 配置文件
ansible.builtin.copy:
dest: /etc/docker/daemon.json
content: |
{
"proxies": {
"http-proxy": "socks5://192.168.200.1:10808",
"https-proxy": "socks5://192.168.200.1:10808",
"no-proxy": "localhost,127.0.0.1"
}
}
owner: root
group: root
mode: '0644'
register: docker_config_result
- name: 如果配置文件发生更改,则重启 Docker
ansible.builtin.service:
name: docker
state: restarted
when: docker_config_result.changed
- name: 启动 docker 服务
ansible.builtin.service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: true
when: docker_install_result.changed
when: docker_repo_file.stat.exists or (docker_repo_added is defined and docker_repo_added)
ready.py 脚本监听一个特定端口(8081),等待新机器通过 cloud-init 发送 /ready 回调请求。
当收到请求时,它会为这台新机器动态生成必要的 Ansible 配置文件(inventory 和 ssh_config),然后按顺序执行预定义的 Ansible Playbook,最后清理临时文件。
vim ready.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import sys
import subprocess
import tempfile
import string
import random
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from pathlib import Path
class ReadyRequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
"""处理 /ready 请求的处理器"""
def do_GET(self):
"""处理 GET 请求"""
if self.path == '/ready':
# 获取请求源 IP
client_ip = self.client_address[0]
print(f"[*] 收到来自 {client_ip} 的请求")
# 生成 SSH 配置
if self.generate_ssh_config(client_ip):
# SSH 配置成功,执行 Ansible playbook
if self.execute_ansible(client_ip):
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'text/plain; charset=utf-8')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write("Configuration successful, Ansible playbooks executed successfully\n".encode('utf-8'))
else:
self.send_response(500)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'text/plain; charset=utf-8')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write("Ansible execution failed\n".encode('utf-8'))
else:
self.send_response(500)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'text/plain; charset=utf-8')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write("SSH configuration generation failed\n".encode('utf-8'))
else:
self.send_response(404)
self.end_headers()
def generate_ssh_config(self, ip):
"""生成并追加 SSH 配置到 ~/.ssh/config"""
try:
# 构建 SSH 配置内容
ssh_config_content = f"""Host {ip}
HostName {ip}
Port 22
User root
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/ssh_key
StrictHostKeyChecking no
"""
# 确保 ~/.ssh 目录存在
ssh_dir = Path.home() / '.ssh'
ssh_dir.mkdir(mode=0o700, exist_ok=True)
# SSH 配置文件路径
ssh_config_path = ssh_dir / 'config'
# 追加配置到文件
with open(ssh_config_path, 'a') as f:
f.write(ssh_config_content)
print(f"[+] SSH 配置已追加到 {ssh_config_path}")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 生成 SSH 配置失败: {e}")
return False
def cleanup_ssh_config(self, ip):
"""清理 SSH config 文件中对应 IP 的配置"""
try:
ssh_dir = Path.home() / '.ssh'
ssh_config_path = ssh_dir / 'config'
if not ssh_config_path.exists():
print(f"[*] SSH 配置文件不存在: {ssh_config_path}")
return
# 读取文件内容
with open(ssh_config_path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 构建要删除的配置块的标识
host_marker = f"Host {ip}"
# 过滤掉对应的配置块
new_lines = []
skip_block = False
for line in lines:
if line.strip().startswith(f"Host {ip}"):
skip_block = True
continue
elif line.strip().startswith("Host ") and skip_block:
skip_block = False
if not skip_block:
new_lines.append(line)
# 写回文件
with open(ssh_config_path, 'w') as f:
f.writelines(new_lines)
print(f"[+] SSH 配置已清理: 移除 Host {ip} 的配置")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 清理 SSH 配置失败: {e}")
def generate_inventory(self, ip):
"""生成 inventory.ini 文件"""
try:
# 生成随机文件名
random_str = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits, k=8))
inventory_name = f"inventory_{random_str}.ini"
inventory_path = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), inventory_name)
# 构建 inventory 内容
inventory_content = f"""[centos]
{ip}
"""
# 写入 inventory 文件
with open(inventory_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(inventory_content)
print(f"[+] Inventory 文件已生成: {inventory_path}")
return inventory_path
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 生成 inventory 文件失败: {e}")
return None
def execute_ansible(self, ip):
"""执行 Ansible playbook"""
try:
# 生成 inventory 文件
inventory_path = self.generate_inventory(ip)
if not inventory_path:
return False
ansible_dir = '/opt/ansible'
# 切换到 Ansible 目录
os.chdir(ansible_dir)
try:
# 执行第一个 playbook
print(f"[*] 执行: ansible-playbook -i {inventory_path} configure_repos.yaml")
result1 = subprocess.run(
['ansible-playbook', '-i', inventory_path, 'configure_repos.yaml'],
timeout=300
)
if result1.returncode != 0:
print(f"[-] configure_repos.yaml 执行失败")
return False
print("[+] configure_repos.yaml 执行成功")
# 执行第二个 playbook
print(f"[*] 执行: ansible-playbook -i {inventory_path} centos_docker_china.yaml")
result2 = subprocess.run(
['ansible-playbook', '-i', inventory_path, 'centos_docker_china.yaml'],
timeout=300
)
if result2.returncode != 0:
print(f"[-] centos_docker_china.yaml 执行失败")
return False
print("[+] centos_docker_china.yaml 执行成功")
# 执行完成后,清理 SSH config 文件中对应的配置
self.cleanup_ssh_config(ip)
return True
finally:
# 删除临时的 inventory 文件
try:
os.remove(inventory_path)
print(f"[+] 临时文件已删除: {inventory_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 删除临时文件失败: {e}")
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
print("[-] Ansible 执行超时")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 执行 Ansible 失败: {e}")
return False
def log_message(self, format, *args):
"""自定义日志输出"""
print(f"[*] {format % args}")
def start_server():
"""启动 HTTP 服务器"""
host = '10.33.1.1'
port = 8081
server_address = (host, port)
httpd = HTTPServer(server_address, ReadyRequestHandler)
print(f"[*] 服务器启动在 http://{host}:{port}")
print(f"[*] 等待请求: GET /ready")
try:
httpd.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n[*] 服务器已停止")
httpd.server_close()
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_server()
为 ready.py 脚本设置权限,并运行脚本。
chmod +x ready.py
./ready.py
测试
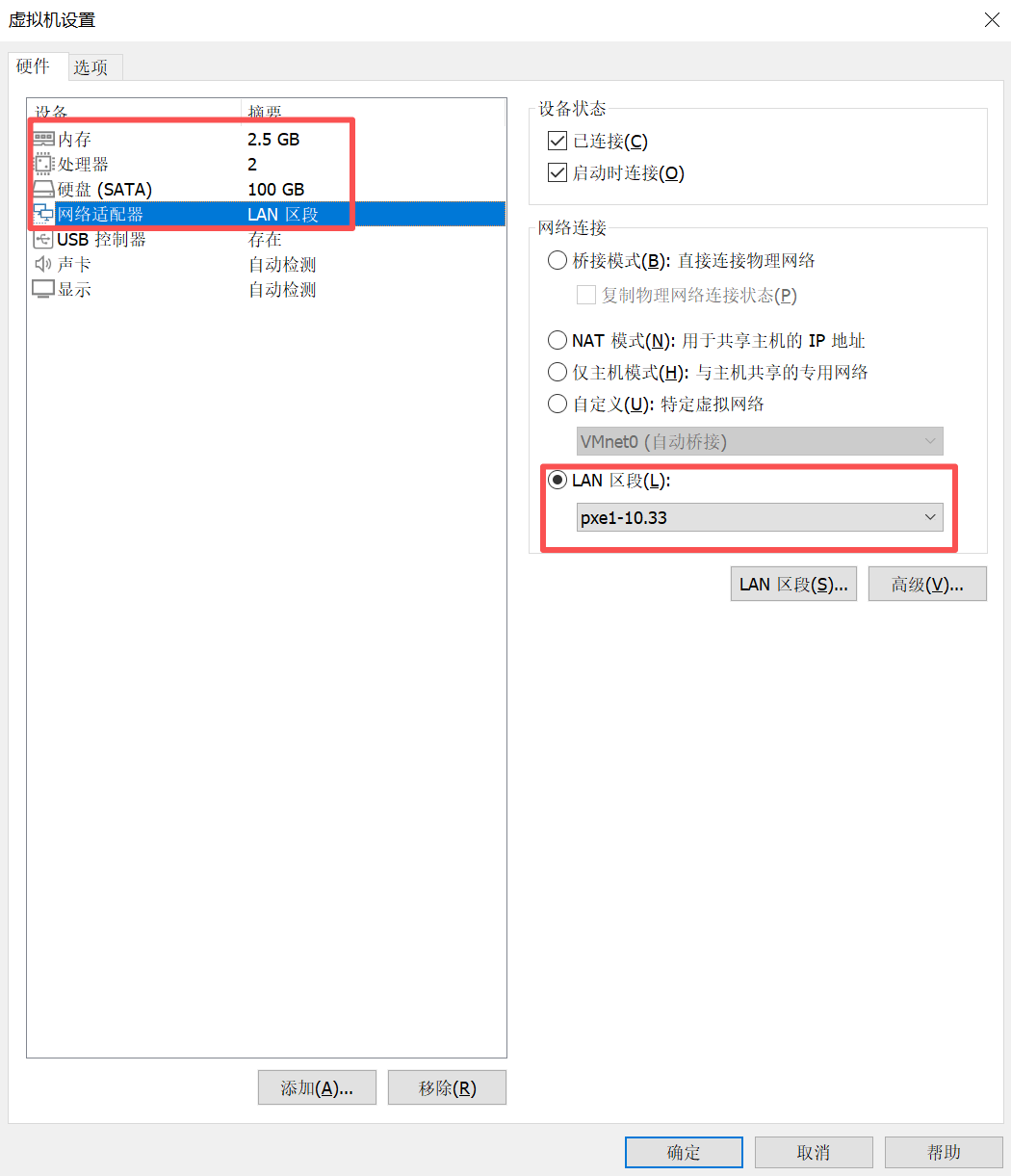
为验证 PXE 自动化部署流程的正确性,需创建一个 VMware 虚拟机,并确保其配置满足以下要求,以保证与 PXE 服务器的兼容性和部署的顺利进行:
- CPU:建议配置至少 2 个 CPU 核心,以确保系统安装和后续配置任务的性能需求。
- 内存:最低 2.5 GB,以支持 Rocky Linux 10.0 的安装和 Cloud-Init、Ansible 等工具的运行。
- 硬盘:分配 100 GB 的磁盘空间,推荐使用精简置备(Thin Provisioning)以节省物理存储,同时确保有足够空间用于操作系统和 Docker 环境。
- 网络适配器:网络适配器必须与 PXE 服务器的 eth1 接口(IP: 10.33.1.1/16)处于同一二层广播域,确保客户端能够通过 DHCP 获取 IP 地址并访问 TFTP 和 HTTP 服务。
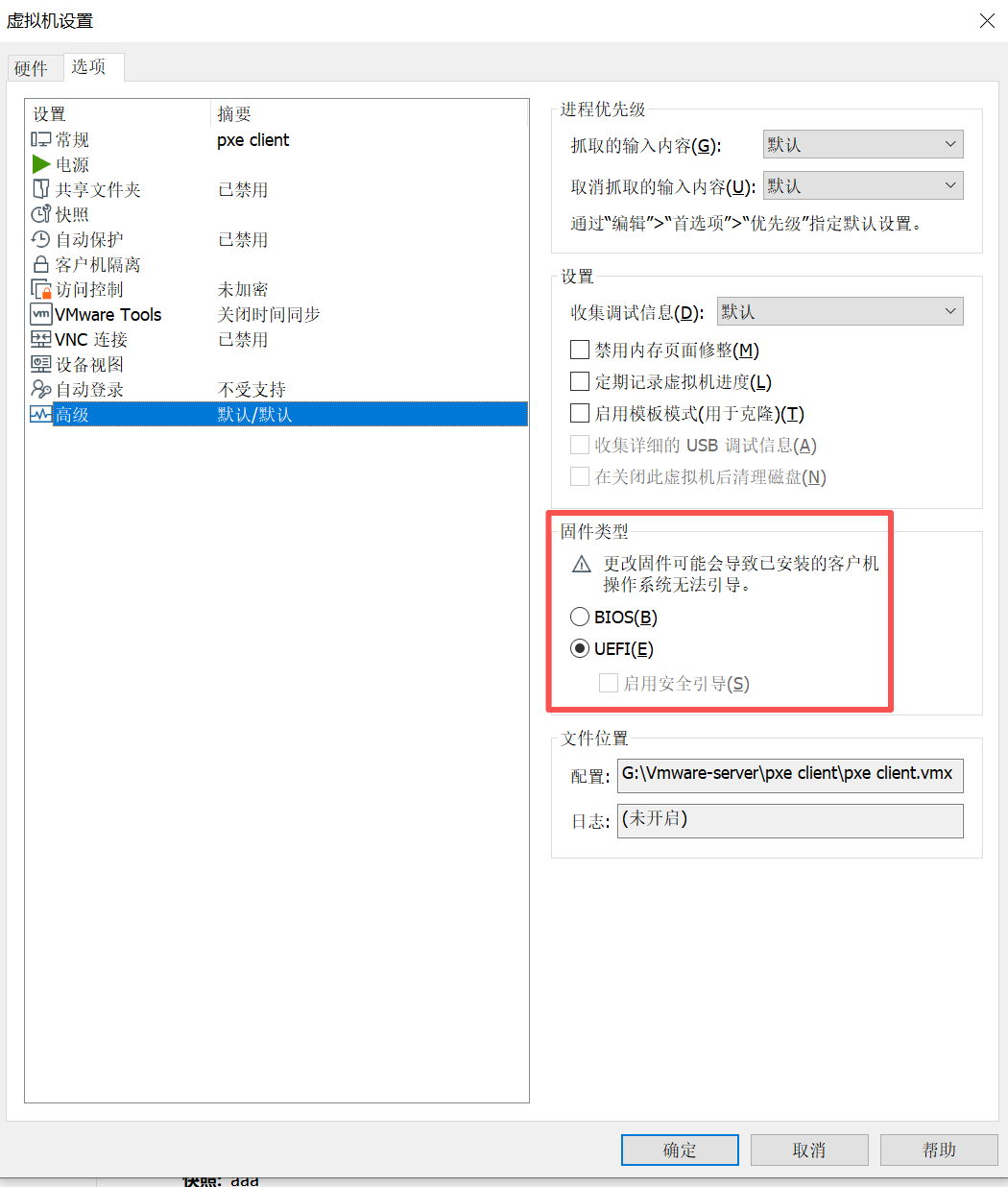
- 固件设置:虚拟机 BIOS 必须配置为 UEFI 模式,因为提供的 Kickstart 文件(anaconda-ks.cfg)针对 UEFI 环境优化,包含 EFI 分区配置(如 /boot/efi)。
开机